Ludwig’s Angina
Ludwig’s Angina is a clinical diagnosis and is the name given to a massive firm cellulites affecting simultaneously the submandibular and sub mental region and the sublingual space bilaterally.
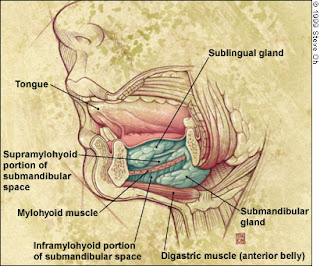
It usually arises from a submandibular space infection caused by a principal infection or pericoronitis.
around the lower 3rd molar. Then the infection spread to the sublingual space on the same side. From there it passes to the opposite sublingual space and to the contra lateral submandibular region. The sub mental space is involved by lymphatic spread. This serious condition can also develop in a converse manner.
2. Intraoral swelling distends the floor of the mouth & forces the tongue up against the palate protrude the tongue from mouth.
3. Deglutition & speech are difficult with progressive dyspnoea (respiratory obstruction due to backwards spread of infection) caused by tongue.
4. The patient is very ill with marked pyrexia.
5. In untreated case, edema of the glottis causes a complete respiratory obstruction. A fatal termination can occur in 12-24hours in untreated case.
2. Drainage of pus as early as possible by incision.
3. Higher antibiotic>immediate i/v infusion of 500mg of metronidazol & 500mg of amoxicillin 8 hourly usually brings about rapid improvement.
4. If allergic to penicillin erythromycin lactobionate 600mg given slowly i/v 8 hourly or 80mg gentamycin i/m.
5. Administration of oxygen after tracheotomy sign of respiratory obstruction found.
6. The causative tooth should be extracted as soon as patient’s condition improves.
Ludwig’s Angina is a clinical diagnosis and is the name given to a massive firm cellulites affecting simultaneously the submandibular and sub mental region and the sublingual space bilaterally.
Etiology of Ludwig’s Angina

around the lower 3rd molar. Then the infection spread to the sublingual space on the same side. From there it passes to the opposite sublingual space and to the contra lateral submandibular region. The sub mental space is involved by lymphatic spread. This serious condition can also develop in a converse manner.
Clinical Features of Ludwigs Angina:
1. Painful, massive firm board like swelling (wooden hardness) of the upper part of the neck & floor of the mouth.2. Intraoral swelling distends the floor of the mouth & forces the tongue up against the palate protrude the tongue from mouth.
3. Deglutition & speech are difficult with progressive dyspnoea (respiratory obstruction due to backwards spread of infection) caused by tongue.
4. The patient is very ill with marked pyrexia.
5. In untreated case, edema of the glottis causes a complete respiratory obstruction. A fatal termination can occur in 12-24hours in untreated case.
Treatment of Ludwigs Angina
1. Immediate hospitalization.2. Drainage of pus as early as possible by incision.
3. Higher antibiotic>immediate i/v infusion of 500mg of metronidazol & 500mg of amoxicillin 8 hourly usually brings about rapid improvement.
4. If allergic to penicillin erythromycin lactobionate 600mg given slowly i/v 8 hourly or 80mg gentamycin i/m.
5. Administration of oxygen after tracheotomy sign of respiratory obstruction found.
6. The causative tooth should be extracted as soon as patient’s condition improves.












0 comments:
Post a Comment